Sign up to receive news from ICE Knowledge direct to your inbox.
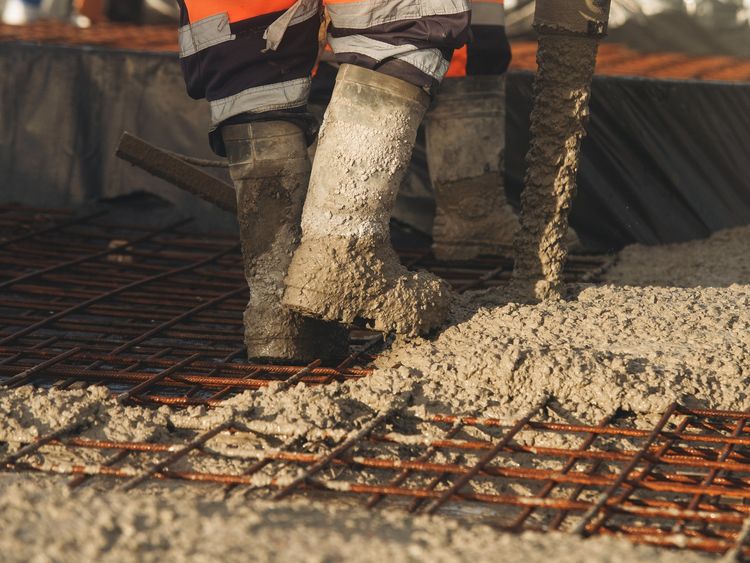
The construction industry could help the UK to make great strides towards its net zero goals by adopting calcined clay extensively as a low-carbon cementitious material.
That was the view of two leading materials experts who spoke at the autumn meeting of the ICE’s Decarbonisation Community Forum.
Dr Pete Winslow, director at Expedition Engineering, and Jon Knights, materials and durability lead at High Speed 2, stressed that calcined clay could be used to form a much less carbon-intensive cement than the industry’s most popular mixes. They also highlighted the main barriers to its widespread uptake – and set out recommendations for overcoming these.
The most widely used cement by far in the UK is Portland cement, especially as a key component of concrete. Portland cement mostly comprises clinker. Producing clinker, by heating limestone and other minerals to high temperatures in a kiln, releases large volumes of carbon dioxide.
Methods to reduce this concrete related carbon are already established, typically by replacing cement with ground granulated blast furnace slag (GGBS) or pulverised fly ash (PFA). Both GGBS and PFA are byproducts of carbon-intensive industrial processes but with a move towards greener practices — notably with the shut down of coal power stations and an increased re-use of steel — the availability of GGBS and PFA is declining. The development of new alternatives are vital to help fill this void.
Calcined clay is one promising option that has the potential to replace up to half of a cement mix's clinker content. It is “a mature technology, with over 120 years of recorded use in construction”, according to Knights. He noted that its use in cement and concrete could reduce a building project’s overall carbon footprint by as much as 50%.

Adopting calcined clay as a cementitious material could significantly reduce the carbon footprint of the construction sector
UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Linking our work back to the UN SDGs is a core part of the ICE’s plan and mission. This content ties in with the following SDGs:
- SDG 9: Industry, innovation and infrastructure

- SDG 11: Sustainable cities and communities

- SDG 13: Climate action